It was Albert Einstein who said he knows why so many people love chopping wood.
They immediately see the results.
But project planning is more than chopping wood and its integral part is project scheduling that must describe the future as realistic as much. Very often it is a trial and error process of adjusting tasks to constraints or resources.
How do experienced project managers meet these tasks?
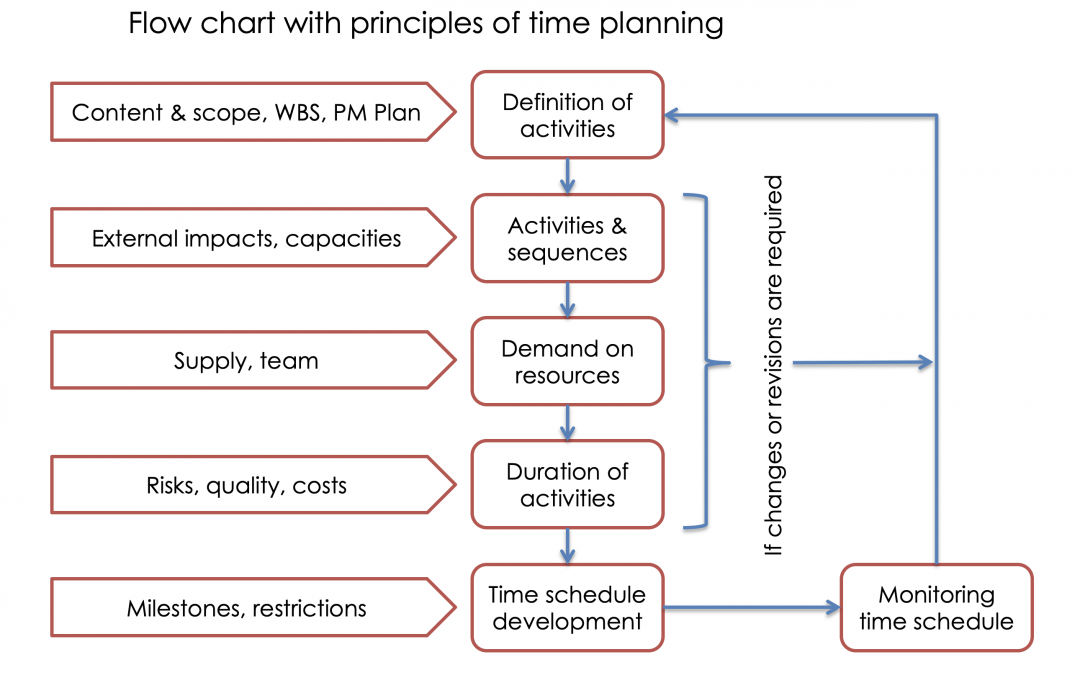
Here are some key words describing the steps of time scheduling. The processes of time scheduling and management is a summery of
- Definition of activities (work)
- Analysing & definition of procedures & dependencies
- Estimation of resources demand
- Estimation of duration & sequences
- Developing a time schedule
- Monitoring of the time schedule
For each of the six processes above the responsible project manager must evaluate
Input data
- What affects the time planning?
Instruments and methods
- What is available?
Output data
- What is intended by the time schedule?
Time scheduling interacts with the estimation of resources demand.
Answer the following W-questions as good as much and you will get robust results that finally form the basis of the core element of scheduling.
- What is required?
- When is something required?
- Which quantity is required?
- Where is it required?
- Which quality standard is required?
- What time period are resources required?
The next hurdle in the process of time scheduling is estimation of duration of activities.
This is without doubt the most difficult part of time scheduling and needs extensive
- Experience of people in charge
- Comprehensive data or database
- Detailed records of lessons learned
- Last but not least reality – no phantasy
All the activities listed above are single tasks required for scheduling. Describing the future work process as realistic as much with considering uncertainties as good as much one element is the absolutely basis for successful time scheduling.
Prepare a carefully and well-done Work Breakdown Structure (WBS)
It will help in analysing of
- What time requires an activity – work package– sub project?
- What are the interdependencies and how do they interact?
The essential requirements for time scheduling are
Estimation and limitation of
- Demand (material, men, machinery)
- Dependencies (what affects what?)
- Duration (time)
These are parameters with high uncertainty factors.
Consequently clarify dependencies of activities before you start
- Which activity is first
- Which activity is after
- Which activities could go parallel
- Each activity has minimum one previous and one after
- The activity START has only successors
- The activity END has only predecessors
Three types of relations or dependencies determine time planning
- Mandatory (i.g. formwork – concrete)
- Discretionary (i.g. Depending on capacity)
- External (i.g. wheather, politics)
The activity sequencing is as follows
- Finish-to-Start: successor depends on finish of predecessor
- Finish-to-Finish: finish successor depends on finish predecessor
- Start-to-Start: start successor depends on start predecessor
- Start-to-Finish: finish successor depends on start predecessor